Lab0:wamup 手动联网: 通过telnet获取
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 telnet cs144.keithw.org 80 Trying 104.196.238.229... Connected to cs144.keithw.org. Escape character is '^]'. GET /hello HTTP/1.1 Host: cs144.keithw.org Connection: close HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Tue, 12 Nov 2024 05:17:24 GMT Server: Apache Last-Modified: Thu, 13 Dec 2018 15:45:29 GMT ETag: "e-57ce93446cb64" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 14 Connection: close Content-Type: text/plain Hello, CS144! Connection closed by foreign host.
nc命令使用,开两个窗口
nc -l -p 9090
telnet localhost 9090
webget 尽最大努力传输数据
获取源码:git clone https://github.com/cs144/minnow
编译源码:cmake -S . -B build && cmake --build build(需要3.24以上版本)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 void get_URL ( const string& host, const string& path ) TCPSocket sock {}; sock.connect ( Address ( host, "http" ) ); string message = "GET " +path+" HTTP/1.1\r\n" ; message += "Host: " +host+"\r\n" ; message +="Connection: close\r\n\r\n" ; sock.write (message) while ( !sock.eof () ) { cout << sock.read (); } sock.close (); return ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 make ./apps/webget cs144.keithw.org /hello cmake --build build --target check_webget ben% cmake --build build --target check_webget Test project /home/ben/cpp/minnow/build Start 1: compile with bug-checkers 1/2 Test #1: compile with bug-checkers ........ Passed 0.48 sec Start 2: t_webget 2/2 Test #2: t_webget ......................... Passed 1.05 sec 100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 2 Total Test time (real) = 1.53 sec Built target check_webget
An in-memory reliable byte stream 这里用了queue容器来实现,push和pop刚好符号容器特点,同时peek重复读取front()
我原先是用queue< char >实现的,代码简单,但是每一次push为时间复杂度O(n)了,如果用deque< string >,然后添加一个stored_来保存size,push就为O(1)的
但是如果用,pop实现就有问题,因front()返回的是拷贝数据,而pop出的len有可能front()的一个string小,那只能to_delete记录待删除的,等够一个string了再一起删除,而这时候要注意peek()从to_delete读取下一个字符
后来发现影响speed的是peek,由于存储char每次只能读出一个字符,而存储string每次能提前读出字符串
细节:要注意erro状态,我认为在writer,即使erro依然可以写,因为不知道erro是什么原因;而在reader,erro一定不能读
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 #include "byte_stream.hh" using namespace std;ByteStream::ByteStream ( uint64_t capacity ) : capacity_ ( capacity ) {} bool Writer::is_closed () const return close_; } void Writer::push ( string data ) if (is_closed () || data.empty () || available_capacity () == 0 ) return ; if (data.length () > available_capacity ()) data.resize (available_capacity ()); bytes_buffered_+=data.length (); bytes_pushed_ += data.length (); stream_.push (std::move (data)); return ; } void Writer::close () close_ = true ; } uint64_t Writer::available_capacity () const return capacity_ - bytes_buffered_; } uint64_t Writer::bytes_pushed () const return bytes_pushed_; } bool Reader::is_finished () const return close_ && bytes_buffered_ == 0 ; } uint64_t Reader::bytes_popped () const return bytes_popped_; } string_view Reader::peek () const if (bytes_buffered_ == 0 ) return {}; return string_view (stream_.front ()).substr (to_delete); } void Reader::pop ( uint64_t len ) bytes_buffered_ -= len; bytes_popped_ += len; while (len != 0U ) { const uint64_t & size = stream_.front ().length () - to_delete; if (len < size) { to_delete += len; break ; } stream_.pop (); len -= size; to_delete = 0 ; } } uint64_t Reader::bytes_buffered () const return bytes_buffered_; }
结果speed也是从0.5——>11Gbit/s
有时候莫名其妙段错误,从网上找到的方法
禁止Linux地址空间布局随机化 ASLR 。
1 echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Test project /home/ben/cpp/minnow/build Start 1: compile with bug-checkers 1/10 Test #1: compile with bug-checkers ........ Passed 3.49 sec Start 2: t_webget 2/10 Test #2: t_webget ......................... Passed 1.08 sec Start 3: byte_stream_basics 3/10 Test #3: byte_stream_basics ............... Passed 0.02 sec Start 4: byte_stream_capacity 4/10 Test #4: byte_stream_capacity ............. Passed 0.01 sec Start 5: byte_stream_one_write 5/10 Test #5: byte_stream_one_write ............ Passed 0.02 sec Start 6: byte_stream_two_writes 6/10 Test #6: byte_stream_two_writes ........... Passed 0.02 sec Start 7: byte_stream_many_writes 7/10 Test #7: byte_stream_many_writes .......... Passed 0.05 sec Start 8: byte_stream_stress_test 8/10 Test #8: byte_stream_stress_test .......... Passed 0.13 sec Start 37: compile with optimization 9/10 Test #37: compile with optimization ........ Passed 0.80 sec Start 38: byte_stream_speed_test ByteStream throughput: 11.40 Gbit/s 10/10 Test #38: byte_stream_speed_test ........... Passed 0.09 sec 100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 10 Total Test time (real) = 5.70 sec
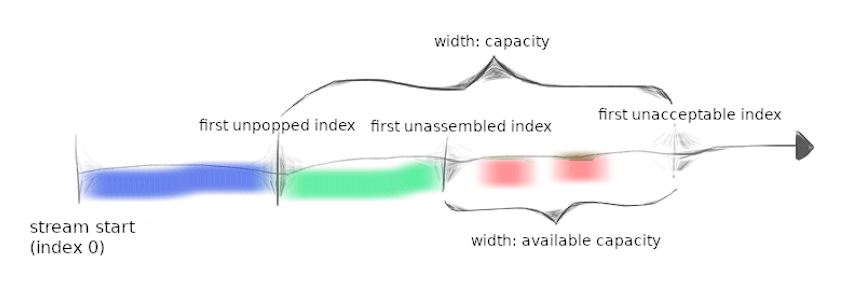
Lab1:stitching substrings into a byte stream 流重组器
绿色:stored in stream
粉色:reassembler_available_capacity
首先应该排除两边不在边界的两种情况,然后再根据需要对data进行分片
颜色均摊(odt老司机树): 使用平衡树或链表处理区间覆盖问题
split(int x): 从[l, r)切割[l, x), [x, r),返回第二个迭代器
细节注意:
split实现 :split是reassembler的核心了,你需要至少考虑下来几个问题:
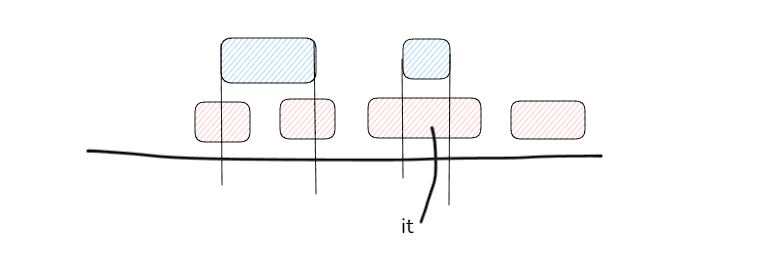
split边界判断:为x或者it==odt.begin()直接返回,x是否在区间里:| —- l —- r | 倘若这种情况应该返回++it,而在str区间才考虑分割
迭代器失效问题:先split(r)再split(l),只有先split(r)后,it变为it+1了,才不会失效,即确保l<=r —> it_l <= it_r,如图it可能被删除
关闭流:当is_last_substring==true不能直接close,因为数据可能还没拼接完,应当有一个end_index_来记录is_last_substrings的位置,并且end_index可能大于available_capacity
这里用set实现,关注顺序的话用map实际会更好,因为底层都是红黑树,所以可以看作都是有序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private : struct Node_t { uint64_t l; uint64_t r; std::string v; bool operator <(const Node_t& b) const {return l < b.l;} }; ByteStream output_; std::set<Node_t> odt{}; uint64_t bytes_pending_{}; std::vector<uint64_t > end_index_{}; auto split (uint64_t x)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 #include "reassembler.hh" #include <iostream> using namespace std;auto Reassembler::split (uint64_t x) auto it = odt.lower_bound (Node_t{x, 0 , "" }); if (it != odt.end () && it->l == x) return it; if (it == odt.begin ()) return it; --it; uint64_t l = it->l, r = it->r; string v = it->v; if (r > x) { odt.erase (it); odt.insert (Node_t (l, x, v.substr (0 ,x-l))); return odt.insert (Node_t (x, r, v.substr (x-l))).first; } return ++it; } void Reassembler::insert ( uint64_t first_index, string data, bool is_last_substring) auto do_close = [&]{ if (!end_index_.empty () && end_index_.front () == writer ().bytes_pushed ()) output_.writer ().close (); }; if (writer ().is_closed () || writer ().available_capacity () == 0U ) return ; if (data.empty () && is_last_substring && end_index_.empty ()) { end_index_.push_back (first_index); return do_close (); } if (!end_index_.empty () && first_index >= end_index_.front ()) return do_close (); uint64_t first_unassembled_index = writer ().bytes_pushed (); uint64_t first_unacceptable_index = first_unassembled_index + writer ().available_capacity (); if (first_index >= first_unacceptable_index ||first_index + data.length () <= first_unassembled_index) return ; if (first_index < first_unassembled_index) { data.erase (0 , first_unassembled_index - first_index); first_index = first_unassembled_index; } if (is_last_substring && end_index_.empty ()) end_index_.push_back (first_index + data.length ()); if (first_index + data.length () > first_unacceptable_index) data.resize (first_unacceptable_index - first_index); uint64_t l = first_index, r = first_index + data.length (); auto it_r = split (r); auto it_l = split (l); for (auto i = it_l; i != it_r; ++i) bytes_pending_ -= i->r - i->l; odt.erase (it_l, it_r); odt.insert ({l,r,data}); bytes_pending_ += r-l; auto it = odt.begin (); while (it->l == writer ().bytes_pushed () && it != odt.end ()) { bytes_pending_ -= it->r -it->l; output_.writer ().push (it->v); it = odt.erase (it); } do_close (); } uint64_t Reassembler::bytes_pending () const return bytes_pending_; }
对比最快接近10Gbit/s感觉还是有点慢
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 ... Start 9: reassembler_single 8/17 Test #9: reassembler_single ............... Passed 0.01 sec Start 10: reassembler_cap 9/17 Test #10: reassembler_cap .................. Passed 0.02 sec Start 11: reassembler_seq 10/17 Test #11: reassembler_seq .................. Passed 0.02 sec Start 12: reassembler_dup 11/17 Test #12: reassembler_dup .................. Passed 0.04 sec Start 13: reassembler_holes 12/17 Test #13: reassembler_holes ................ Passed 0.02 sec Start 14: reassembler_overlapping 13/17 Test #14: reassembler_overlapping .......... Passed 0.03 sec Start 15: reassembler_win 14/17 Test #15: reassembler_win .................. Passed 0.34 sec Start 37: compile with optimization 15/17 Test #37: compile with optimization ........ Passed 0.14 sec Start 38: byte_stream_speed_test ByteStream throughput: 10.57 Gbit/s 16/17 Test #38: byte_stream_speed_test ........... Passed 0.09 sec Start 39: reassembler_speed_test Reassembler throughput: 5.47 Gbit/s 17/17 Test #39: reassembler_speed_test ........... Passed 0.19 sec 100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 17
Lab2:TCP receiver 你需要实现
ackno
window size
三点:
32bit环绕64bit,取模操作
seqnos随机开始,即SYN,rboustness and no as same with old
SYN和FIN各占一个seqno,确保可靠接收数据头尾
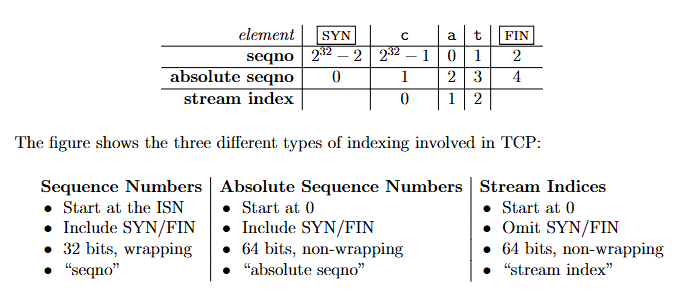
1、64bit index和32bit seqnos相互转换 三种序号:
注意:
这里zero_point是SYN不是seqno为0,checkpoint是接收方当前期望的数据位置,将使用第一个未组装的索引值
如果一个ISN为0,seqno为17,则absolute seqno可能为17,2^32+17,2^33+17,2^32+2^33+17……
32bit转换64bit除了加上checkpoint高32位偏移之外,你还需考虑res和checkpoint的距离,这里我认为res每次偏移BASE_(2^32),有以下两种情况
—–check-2^16——–check——-check+2^16—–
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include "wrapping_integers.hh" using namespace std;Wrap32 Wrap32::wrap ( uint64_t n, Wrap32 zero_point ) return zero_point + static_cast <uint32_t >(n); } uint64_t Wrap32::unwrap ( Wrap32 zero_point, uint64_t checkpoint ) const const uint64_t a = raw_value_ - zero_point.raw_value_; uint64_t res = (checkpoint & ~(BASE_-1 )) | a; if (res >= BASE_ && res > checkpoint+BASE_/2 ) res -= BASE_; if (res+BASE_/2 < checkpoint) res+=BASE_; return res; }
2、tcp receiver 任务:
接收Tcp message解析并插入流中
生成ack包
SYN和FIN本身占一位seqno,且不属于流
window_size最大UINT16_MAX
接收到RST说明流错误不能读,写错误则发送RST
转换时注意:
stream=ab_seqno-1
checkpoint应该去哪找?应该找已经push的stream_index
思考:假如接收时跳过了一个数据包,后面陆续接收了许多个数据包,但是他们却都用同一个checkpoint,因为中间有空缺不能push,会发送覆盖吗?
发现window_size最大UINT_MAX,而我在做seqno转换的时候发现checkpoint每次最小偏移2^32,也就是说还窗口为0时不能看你跳到下一个checkpoint
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 #include "tcp_receiver.hh" using namespace std;void TCPReceiver::receive ( TCPSenderMessage message ) if (writer ().has_error () && writer ().is_closed ()) return ; if (message.RST) { reader ().set_error (); return ; } if (!zero_point.has_value ()) { if (!message.SYN) return ; zero_point.emplace (message.seqno); } const uint64_t checkpoint = writer ().bytes_pushed () + 1 ; const uint64_t SYN_absolute_seqno = message.seqno.unwrap (zero_point.value (), checkpoint); const uint64_t stream_index = SYN_absolute_seqno - 1 + static_cast <uint64_t >( message.SYN ); reassembler_.insert (stream_index , move (message.payload), message.FIN); } TCPReceiverMessage TCPReceiver::send () const uint64_t MAX_UINT16 = (1LL << 16 ) - 1 ; uint16_t wsize{ static_cast <uint16_t >(writer ().available_capacity () >= MAX_UINT16 ? MAX_UINT16 : writer ().available_capacity ())}; bool RST{writer ().has_error ()}; if (zero_point.has_value ()) { uint64_t n = writer ().bytes_pushed () + 1LL + static_cast <uint64_t >( writer ().is_closed ()) ; return {Wrap32::wrap (n, zero_point.value ()), wsize, RST}; } return {nullopt , wsize, RST}; }
ack是optional对象,为空时应该传递nullopt
Lab3 tcp sender 实现两个模块:发送方和计时器
发送方职责:
尽可能填充窗口:维护一个队列存放outstanding数据,维护window_left和next_ab_seqno下一个要发送的序列号
跟踪对方acknos和窗口大小:维护window窗口大小,当接收到ack大于等于窗口滑动一次的window_left时pop,窗口每次滑动距离为队首包长度
ARQ:automatic repeat request by tick() until ack
在这次lab需要自己实现一个重传计数器,并且你的时间计时只能通过tick来传入走过的时间,以下是实现规则:
每隔几毫秒,您的 TCPSender 的 tick 方法将被调用,并带有一个参数,该参数告诉它自上次调用该方法以来已经过去了多少毫秒。使用它来维护 TCPSender 的总毫秒数
在构造 TCPSender 时,会给它一个参数,告诉它重新传输超时 (RTO) 的“初始值”。RTO 是在重新发送未完成的 TCP 分段之前等待的毫秒数。RTO 的值会随着时间的推移而变化,但 “初始值” 保持不变。起始代码将 RTO 的“初始值”保存在名为 initial RTO ms 的成员变量中。
您将实施重新传输计时器:可以在特定时间启动的警报,一旦 RTO 过后,警报就会响起(或“过期”)。我们强调,这种时间流逝的概念来自被调用的 tick 方法,而不是通过获取一天中的实际时间。
每次发送包含数据(序列空间中的非零长度)的段时(无论是第一次还是重新传输),如果计时器未运行,请启动它运行,以便它在 RTO 毫秒后过期(对于 RTO 的当前值)。“过期”是指将来的时间将用完一定的毫秒数。
确认所有未完成数据后,停止重传计时器。
if tick and RTO
a:重传,你需要缓存未完成区段
b:窗口大小非0:
跟踪连续重传次数,到达一定值终止
指数回退:RTO翻倍
c:重置计时器并启动它
接收到ackno后:
重置RTO
若发送方有未完成数据,重新传输计时器
consecutive retransmissions置零
总结遇到的问题:
SYN不应发送数据
FIN发送条件:流已完成并且要占用一个窗口
发送不完全:push应该一直发送,直到window为0,或流为0;所以应该套个循环
矛盾的测试案例:The test “SYN + FIN”
这里明明没有收到SYN,windowsize=0,还要能同时发送SYN和FIN,只能特殊处理了
1 2 3 4 5 if (msg.SYN && new_window_size_ == 1 && reader ().is_finished ()){ msg.FIN = true ; FIN = true ; }
后来发现:这是测试空ack_no的,收到一个空的ack_no,应该改变windowsize,而不是直接返回,于是代码一改再改
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 #pragma once #include "byte_stream.hh" #include "tcp_receiver_message.hh" #include "tcp_sender_message.hh" #include <cstdint> #include <functional> #include <list> #include <memory> #include <optional> #include <queue> class RetransmissionTimer { public : void reload (uint64_t initial_RTO_ms_) void tick (uint64_t ms_since_last_tick) void reset () 0 ; } bool is_expired () return timer_ >= RTO_ms_; } void double_RTO () void start () true ; reset (); } void stop () false ; } bool is_start () return start_; } private : bool start_{}; uint64_t timer_{}; uint64_t RTO_ms_{}; }; class TCPSender { public : TCPSender ( ByteStream&& input, Wrap32 isn, uint64_t initial_RTO_ms ) : input_ ( std::move ( input ) ), isn_ ( isn ), initial_RTO_ms_ ( initial_RTO_ms ) {} TCPSenderMessage make_empty_message () const ; void receive ( const TCPReceiverMessage& msg ) using TransmitFunction = std::function<void ( const TCPSenderMessage& )>; void push ( const TransmitFunction& transmit ) void tick ( uint64_t ms_since_last_tick, const TransmitFunction& transmit ) uint64_t sequence_numbers_in_flight () const uint64_t consecutive_retransmissions () const Writer& writer () { return input_.writer (); } const Writer& writer () const return input_.writer (); } const Reader& reader () const return input_.reader (); } private : ByteStream input_; Wrap32 isn_; uint64_t initial_RTO_ms_; std::queue<TCPSenderMessage> outstanding_message_{}; uint64_t retransmission_count{}; uint64_t outstanding_count{}; uint16_t window_size_{1 }; RetransmissionTimer Timer_{}; bool SYN{}; bool FIN{}; uint64_t next_ab_seqno{}; uint64_t window_left{}; };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 #include "tcp_sender.hh" #include "tcp_config.hh" using namespace std;uint64_t TCPSender::sequence_numbers_in_flight () const return outstanding_count; } uint64_t TCPSender::consecutive_retransmissions () const return retransmission_count; } void TCPSender::push ( const TransmitFunction& transmit ) uint64_t new_window_size_ = window_size_ == 0 ? 1 : window_size_; while (new_window_size_ > outstanding_count) { if (FIN) return ; auto msg {make_empty_message ()}; if (!SYN) { msg.SYN = true ; SYN = true ; } auto & payload = msg.payload; uint64_t len = min (TCPConfig::MAX_PAYLOAD_SIZE, new_window_size_ - outstanding_count); while (payload.size () < len && reader ().bytes_buffered () != 0 ) { string_view view { reader ().peek () }; view = view.substr ( 0 , len - payload.size () ); payload += view; input_.reader ().pop ( view.size () ); } if ( !FIN && new_window_size_ > outstanding_count + msg.sequence_length () && reader ().is_finished () ) { msg.FIN = true ; FIN = true ; } if (msg.sequence_length () == 0 ) return ; transmit (msg); if (!Timer_.is_start ()) { Timer_.start (); Timer_.reload (initial_RTO_ms_); } outstanding_count += msg.sequence_length (); next_ab_seqno += msg.sequence_length (); outstanding_message_.emplace ( move (msg) ); } } TCPSenderMessage TCPSender::make_empty_message () const return {Wrap32::wrap (next_ab_seqno, isn_), false , {}, false , input_.has_error ()}; } void TCPSender::receive ( const TCPReceiverMessage& msg ) if (msg.RST) input_.set_error (); if (input_.has_error ()) return ; window_size_ = msg.window_size; if (!msg.ackno.has_value ()) return ; auto ab_ackno = msg.ackno.value ().unwrap (isn_, next_ab_seqno); if (ab_ackno > next_ab_seqno) return ; bool is_reset = false ; while (!outstanding_message_.empty ()) { auto & mess = outstanding_message_.front (); if ( mess.sequence_length () + window_left > ab_ackno) break ; window_left += mess.sequence_length (); outstanding_count -= mess.sequence_length (); outstanding_message_.pop (); is_reset = true ; } if (is_reset) { Timer_.reload (initial_RTO_ms_); retransmission_count = 0 ; Timer_.stop (); if (!outstanding_message_.empty ()) Timer_.start (); } } void TCPSender::tick ( uint64_t ms_since_last_tick, const TransmitFunction& transmit ) if (!Timer_.is_start ()) return ; Timer_.tick (ms_since_last_tick); if (!Timer_.is_expired ()) return ; if (outstanding_count == 0 ) return ; transmit ( outstanding_message_.front () ); if ( window_size_ != 0 ) { retransmission_count += 1 ; Timer_.double_RTO (); } Timer_.start (); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 Start 21: recv_connect 20/36 Test #21: recv_connect ..................... Passed 0.02 sec Start 22: recv_transmit 21/36 Test #22: recv_transmit .................... Passed 0.45 sec Start 23: recv_window 22/36 Test #23: recv_window ...................... Passed 0.02 sec Start 24: recv_reorder 23/36 Test #24: recv_reorder ..................... Passed 0.02 sec Start 25: recv_reorder_more 24/36 Test #25: recv_reorder_more ................ Passed 1.05 sec Start 26: recv_close 25/36 Test #26: recv_close ....................... Passed 0.02 sec Start 27: recv_special 26/36 Test #27: recv_special ..................... Passed 0.02 sec Start 28: send_connect 27/36 Test #28: send_connect ..................... Passed 0.02 sec Start 29: send_transmit 28/36 Test #29: send_transmit .................... Passed 0.52 sec Start 30: send_retx 29/36 Test #30: send_retx ........................ Passed 0.02 sec Start 31: send_window 30/36 Test #31: send_window ...................... Passed 0.13 sec Start 32: send_ack 31/36 Test #32: send_ack ......................... Passed 0.02 sec Start 33: send_close 32/36 Test #33: send_close ....................... Passed 0.02 sec Start 34: send_extra 33/36 Test #34: send_extra ....................... Passed 0.04 sec Start 37: compile with optimization 34/36 Test #37: compile with optimization ........ Passed 1.23 sec Start 38: byte_stream_speed_test ByteStream throughput: 10.65 Gbit/s 35/36 Test #38: byte_stream_speed_test ........... Passed 0.09 sec Start 39: reassembler_speed_test Reassembler throughput: 5.83 Gbit/s 36/36 Test #39: reassembler_speed_test ........... Passed 0.19 sec 100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 36 Total Test time (real) = 31.57 sec Built target check3
Lab4 Exception: writev: Input/output error
gdb调试发现writev返回-1,errno=5
EIO
I/O 错误,通常是硬件或底层连接问题,或者文件描述符无效。
Lab5:the network interface receive:
IPv4:push queue
ARP:记录ARP表(30秒过期)并回复
send:转换以太网帧,需要实现地址解析
in arp表:发送
not in arp表:放入等待队列,发起arp请求(5秒),
接收的时候有个条件写错了导致一直return,鉴别这个包用了||
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 #include <iostream> #include "arp_message.hh" #include "exception.hh" #include "network_interface.hh" using namespace std;ARPMessage NetworkInterface::make_arp ( const uint16_t opcode, const EthernetAddress target_ethernet_address, const uint32_t & target_ip_address ) ARPMessage arp; arp.opcode = opcode; arp.sender_ethernet_address = ethernet_address_;; arp.sender_ip_address = ip_address_.ipv4_numeric (); arp.target_ethernet_address = target_ethernet_address; arp.target_ip_address = target_ip_address; return arp; } NetworkInterface::NetworkInterface ( string_view name, shared_ptr<OutputPort> port, const EthernetAddress& ethernet_address, const Address& ip_address ) : name_ ( name ) , port_ ( notnull ( "OutputPort" , move ( port ) ) ) , ethernet_address_ ( ethernet_address ) , ip_address_ ( ip_address ) { cerr << "DEBUG: Network interface has Ethernet address " << to_string ( ethernet_address ) << " and IP address " << ip_address.ip () << "\n" ; } void NetworkInterface::send_datagram ( const InternetDatagram& dgram, const Address& next_hop ) uint32_t next_hop_ip = next_hop.ipv4_numeric (); if (ARP_cache_.contains (next_hop_ip)) { auto & dst {ARP_cache_[next_hop_ip].first}; return transmit ( { { dst, ethernet_address_, EthernetHeader::TYPE_IPv4 }, serialize (dgram) } ); } wait_to_send[next_hop_ip].emplace_back (dgram); if (ARP_timer_.contains (next_hop_ip)) return ; ARP_timer_[next_hop_ip] = 0 ; const ARPMessage arp_request { make_arp (ARPMessage::OPCODE_REQUEST, {}, next_hop_ip) }; transmit ( { { ETHERNET_BROADCAST, ethernet_address_, EthernetHeader::TYPE_ARP }, serialize (arp_request)} ); } void NetworkInterface::recv_frame ( const EthernetFrame& frame ) if (frame.header.dst != ethernet_address_ && frame.header.dst != ETHERNET_BROADCAST) return ; if ( frame.header.type == EthernetHeader::TYPE_IPv4 ) { InternetDatagram ipv4_datagram; if ( parse ( ipv4_datagram, frame.payload ) ) { datagrams_received_.emplace ( move ( ipv4_datagram ) ); } return ; } if ( frame.header.type == EthernetHeader::TYPE_ARP ) { ARPMessage msg; parse ( msg, frame.payload ); const uint32_t peer_ip { msg.sender_ip_address }; const EthernetAddress peer_eth { msg.sender_ethernet_address }; ARP_cache_[peer_ip] = { peer_eth, EXPIR_TIME}; if ( msg.opcode == ARPMessage::OPCODE_REQUEST and msg.target_ip_address == ip_address_.ipv4_numeric () ) { const ARPMessage arp_reply { make_arp ( ARPMessage::OPCODE_REPLY, peer_eth, peer_ip) }; transmit ( { { peer_eth, ethernet_address_, EthernetHeader::TYPE_ARP }, serialize ( arp_reply ) } ); } if (wait_to_send.contains (peer_ip)) { auto && list = wait_to_send[peer_ip]; for (auto & dgram:list) transmit ( { { peer_eth, ethernet_address_, EthernetHeader::TYPE_IPv4 }, serialize (dgram) } ); wait_to_send.erase (peer_ip); ARP_timer_.erase (peer_ip); } } } void NetworkInterface::tick ( const size_t ms_since_last_tick ) erase_if (ARP_cache_, [&](auto & it) noexcept { if (it.second.second <= ms_since_last_tick) return true ; it.second.second -= ms_since_last_tick; return false ; }); erase_if (ARP_timer_, [&](auto & it) { it.second += ms_since_last_tick; return it.second >= ARP_TIMEOUT; }); }
Lab6:IP Router 规则:
路由前缀和长度决定ip地址范围
longest-prefix-match
这里用的哈希桶思想,时间复杂度O(n),
匹配为:prefix == ( addr & ~( 1<<(32 - prefix_length) - 1 ) )
umask = 32 - prefix_length
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include "router.hh" #include <bit> #include <cstddef> #include <iostream> #include <optional> #include <ranges> using namespace std;void Router::add_route ( const uint32_t route_prefix, const uint8_t prefix_length, const optional<Address> next_hop, const size_t interface_num ) cerr << "DEBUG: adding route " << Address::from_ipv4_numeric ( route_prefix ).ip () << "/" << static_cast <int >( prefix_length ) << " => " << ( next_hop.has_value () ? next_hop->ip () : "(direct)" ) << " on interface " << interface_num << "\n" ; routing_table_[route_prefix].push_back ( {prefix_length, interface_num, next_hop} ); } void Router::route () for ( const auto & interface : _interfaces ) { auto && datagrams_received { interface->datagrams_received () }; while ( not datagrams_received.empty () ) { InternetDatagram datagram { move ( datagrams_received.front () ) }; datagrams_received.pop (); if ( datagram.header.ttl <= 1 ) { continue ; } datagram.header.ttl -= 1 ; datagram.header.compute_checksum (); const optional<info>& mp { match ( datagram.header.dst ) }; if ( not mp.has_value () ) { continue ; } const auto & [_, num, next_hop] { mp.value () }; _interfaces[num]->send_datagram ( datagram, next_hop.value_or ( Address::from_ipv4_numeric ( datagram.header.dst ) ) ); } } } auto Router::match ( uint32_t addr ) const noexcept -> optional<info> optional<info> res =nullopt ; for (auto & item:routing_table_) { for (auto & i:item.second) { uint8_t umask = 32 - get <0 >(i); uint32_t di = ( addr&~( (1LL << umask) - 1 ) ); if (item.first != di ) continue ; if (res == nullopt || get <0 >(res.value ()) < get <0 >(i)) res = i; } } return res; }
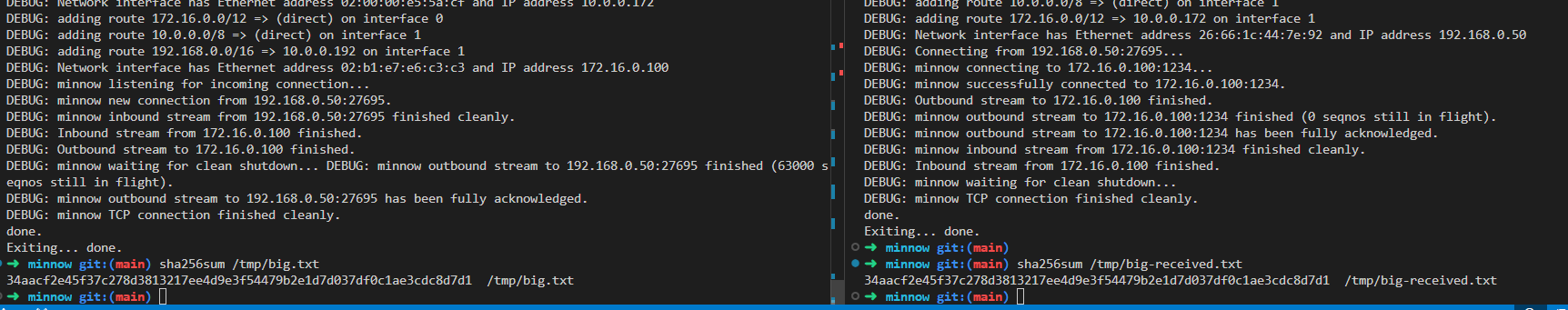
Lab7:整合
验证哈希值,数据正确